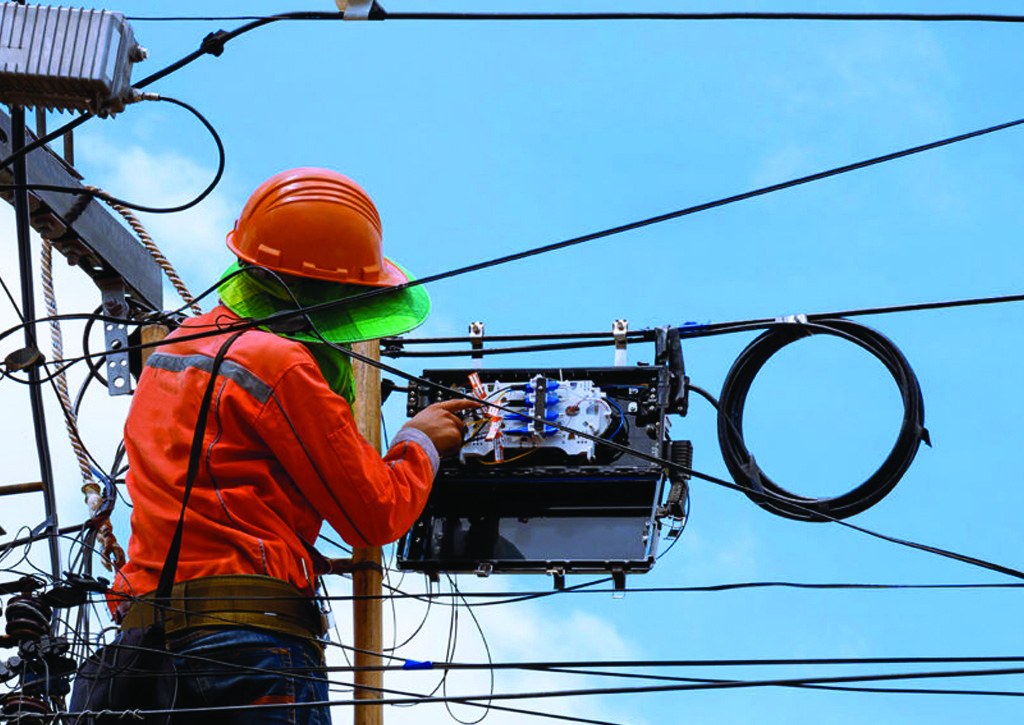
Understanding Fiber Optic Cables:
Fiber optic cables are a type of optical cable that use light to transmit information. These cables have become increasingly popular in the telecom and data communication industries, as they offer higher bandwidth, improved signal quality, improved security, and lower cost than copper wiring alternatives. In order to understand how fiber optics work, it is important to know some basic facts about the technology.
The Science Behind Fiber Optic: How They Work
Fiber optics is a technology that uses light to transmit data over long distances. It is based on the principle of total internal reflection, which means that light rays will bounce off of the walls of a transparent material if the angle of incidence is greater than a certain critical angle.
A fiber optic cable consists of a core made of a material with a high refractive index, such as glass, surrounded by a cladding made of a material with a lower refractive index. When light is injected into the core of a fiber optic cable, it is refracted and bounces off of the walls of the core, traveling down the cable in a straight line.
Here are some additional facts about fiber optics:
- The first fiber optic cable was developed in the early 1960s.
- Fiber optic cable can transmit data at speeds of up to 100 gigabits per second.
- Fiber optic cable is used in the majority of long-distance telecommunications network.
- Fiber optic cable is also used in medical imaging, such as in endoscopes and laser surgery.
Five Cool Uses of Fiber-Optics
Besides providing lightning-speed internet connections, fiber optic cable has many other interesting uses. They could be lighting up the swimming pool at your next vacation rental, or making your new car a little bit smarter.
Many different types of professionals use them as well, from surgeons to artists. Fiber optic cables are even used in satellites and spacecraft! Here are a few uses for fiber optic cable that we think are pretty cool.
1: Space Exploration
Fiber-optic sensors can use light to measure temperature, pressure, rotation, acceleration and more. Satellites and spacecraft use fiber-optics for navigation (gyroscopes) and for exploring their surroundings. In fact, the Mars Rover uses fiber optics to measure and analyze the data it collects.
NASA is currently working on an enhanced fiber optic system with super-fine cables that are only the width of a human hair. In future missions, it will be used as systems monitor for spacecraft landing on the Moon and on Mars.
2: Automotive Safety
Besides being used for lighting in vehicles, fiber optics also help make them safer. The automotive industry uses fiber optic cables to relay messages between different parts of the car. High-speed fiber optic cables eliminate delays in communication so that saftey features like airbags and antilock brakes can activate almost instantaneously.
3: Less Invasive Surgeries
Surgeons use optical cables called endoscopy tubes to light up the surgical site. Because the endoscopy tubes are so slender, they help make surgeries less invasive by allowing for smaller (and fewer) incisions. Medical fiber optics can also be used to guide surgical instruments to precise locations in the body for robotics-assisted procedures.
4: Landscape Lighting
Just like fiber optic cables traverse thousands of miles of the ocean floor, they can also be used underwater on a smaller scale. They’re one of the safest ways to light up swimming pools and water features like fountains, because they don’t conduct any electricity underwater.
5: Fine Art
Fiber optic cables are also used by artists to create mesmerizing installations and fiber arts. In June of 2022, Global Detroit’s Common Bond program organized an exhibit of fiber optic art by women from a wide variety of nationalities and backgrounds, while exploring How is Fiber Optic Internet Installed?
The exhibit included a unity quilt that celebrated Detroit’s diversity. Just like fiber optic cables provide connection to the internet, in the artwork they symbolized connecting immigrants with the rest of the community.
Fiber Optic Cable Advantages and Disadvantages
Fiber optic cables offer a number of advantages over traditional copper cables, including:
- High bandwidth: Fiber optic cables can transmit data at much higher speeds than copper cables.
- Longer distances: Fiber optic cables can transmit data over much longer distances than copper cables without losing signal strength.
- Electromagnetic immunity: Fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, which makes them ideal for use in environments with a lot of electrical noise.
- Security: Fiber optic cables are very difficult to tap, making them a more secure option for transmitting sensitive data.
However, fiber optic cables also have some disadvantages, including:
- Cost: Fiber optic cables are more expensive to produce and install than copper cables.
- Fragility: Fiber optic cables are more fragile than copper cables and can be easily damaged if not handled properly.
- Specialized equipment: Fiber optic cables require specialized equipment for installation and testing.
Types of Fiber Optic Cables
There are several types of fiber optic cables, each designed to meet specific requirements based on the application and environmental factors. The main types of fiber optic cables include:
Single-Mode Fiber (SMF):
Single-mode fiber is designed to carry a single ray of light, which enables it to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal loss. It has a smaller core size (typically around 9 microns) and is commonly used in long-distance applications such as telecommunications, internet backbones, and undersea cables.
Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF):
Multi-mode fiber allows multiple modes (rays) of light to propagate simultaneously through the larger core size (typically 50 or 62.5 microns). Due to this larger core, MMF has higher dispersion, limiting its reach to shorter distances compared to single-mode fiber. It is commonly used in a local area home (LAN), data centers, and shorter-distance communication applications.
Plastic Optical Fiber (POF):
POF is made of plastic materials, which results in a much larger core size (typically 1 mm or larger). POF is less expensive than glass-based fibers and is commonly used in applications like automotive networking, home networks, and short-distance communication systems.
Step-Indexed Fiber:
This type of fiber has a core with a step-index profile, where the refractive index abruptly changes at the core-cladding boundary. It is rarely used in modern applications due to its higher dispersion.
Graded-Indexed Fiber:
Graded-index fiber has a core with a gradual change in refractive index, allowing light rays to travel in curved paths, reducing modal dispersion. It is used in some special applications, but it is less common than single-mode and multi-mode fibers.
What is a Fiber Optic Connector?
Fiber connectors are devices that join two optical fibers together. It allows for the quick and easy connection and disconnection of fiber optic cables, without the need for splicing. Fiber optic connectors are used in a wide variety of applications, including telecommunications, data networking, and medical imaging.
Fiber Optic Networks for Business
In the modern, hyper-connected business landscape, fiber optic networks have emerged as a game-changer. These networks, which transmit data as pulses of light through strands of fiber made from glass or plastic, offer unparalleled speed and reliability. The high bandwidth capacity of fiber optic networks allows for lightning-fast data transfer rates, making them an ideal choice for businesses that rely heavily on data communication. Whether it’s enabling seamless video conferencing, ensuring smooth cloud operations, or supporting high-volume eCommerce transactions, fiber optics deliver the robust performance businesses need to stay competitive. Furthermore, unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optic networks are resistant to electromagnetic interference, ensuring secure and stable connectivity. In essence, investing in fiber optic networks is not just about upgrading your infrastructure—it’s about future-proofing your business in an increasingly digital world. Business internet providers play a crucial role in facilitating this transition, ensuring seamless integration and optimal performance to meet the evolving needs of modern enterprises.
The Role of Fiber Optics in Achieving High-Speed Internet
Fiber optics is the technology that enables high-speed internet. It uses light to transmit data, which is much faster than traditional copper cables. Fiber optic cables can transmit data at speeds of up to 100 gigabits per second, which is enough to support even the most demanding applications.
Fiber optics is used in the backbone of the internet, as well as in the last mile to connect homes and businesses. As the demand for high-speed internet continues to grow, fiber optics will become even more important.
Fiber Optics Connect the World
Fiber optics are more amazing than you might think! Primarily used in telecommunications, fiber optic networks currently provide internet speeds of up to 1Tbs! They span oceans as well as continents and help power satellites in space. As technology advances, we’re sure that there will be even more cool uses for fiber optics in the future.